- Project 1
A Comprehensive Study on Response and Feedback of Asian Forest Soil Carbon Flux to Global Warming
アジアの森林土壌有機炭素放出の温暖化影響とフィードバック効果に関する包括的研究 (2-1705)
PI: Naishen Liang
It is funded by the Global Environment Research Fund (2-1705) of Japan’s Ministry of the Environment, 2017-2020, 47,000,000JY/year)
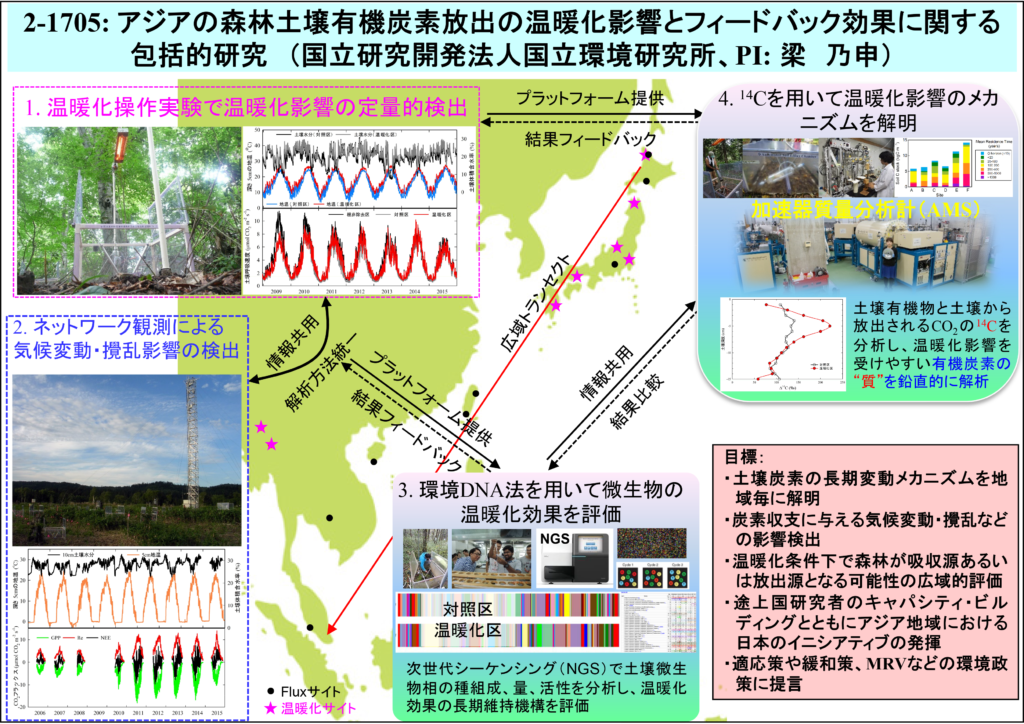
世界気候研究計画(WCRP)に設けられた結合モデル開発作業部会(WGCM)が策定した、第5期結合モデル相互比較計画(CMIP5)では、地球温暖化に伴う土壌呼吸の正のフィードバック効果により、熱帯と中緯度における陸域のCO2吸収能は低下すると予測されている。一方で、モデルの長期予測を検証できる実測データはほとんど無いというのが現状である。最近のNature誌に発表された論文では、世界49地点の温暖化操作実験のデータに基づいて、地球規模の土壌有機炭素の将来予測を行った。2℃の長期目標に沿った場合、2050年の時点で全陸域土壌表層10cmの有機炭素は最大105 Gt失われると推定された。しかしながら、ここで用いられた観測データは、西ヨーロッパを除く、ユーラシア大陸やアジア太平洋地域では、2ヶ所の観測データしか無かった。したがって、温暖化や攪乱などの環境変動下における生態系の応答予測のため、特にアジア地域を中心とした広域的なデータ集積を早急に開始する必要性がある。
本研究内容としては、(1)国立環境研究所が開発・推進している世界最大規模のチャンバー観測ネットワークを用いて、北海道の最北端(北緯45°)から赤道付近のマレーシアまでの広域トランセクトに沿って、代表的な森林生態系における土壌呼吸の連続測定を実施する。それによって、気候変動や攪乱が、各森林生態系の炭素循環に与える影響を定量的に把握する。(2)一部のサイトにおいて赤外線ヒーターを用いた温暖化操作実験を行い、土壌有機炭素分解の温暖化に対する反応を定量的に評価する。(3) 環境DNA法を用いて、気候帯や温暖化処理の有無が土壌微生物相やその動態に及ぼす影響を把握し、温暖化効果の長期維持メカニズムを解明する。(4) 土壌放射性炭素(14C)の分析から、土壌の画分毎の有機炭素の蓄積歴及び長期的な温暖化環境下での分解メカニズムを解明する。(5)多地点の長期観測データと土壌有機炭素分解に関する詳細な情報を基に、複数の既存土壌呼吸モデルの比較解析を行い、気候変動や攪乱に対する陸域炭素循環の応答、フィードバック効果の将来予測精度向上に役立てる(図)。
- Project 2
Evaluation of soil CO2 efflux of Asian Forest Ecosystems based on an automated chamber network
PI: Naishen Liang
It is funded by National Institute for Environmental Studies of Japan (the NIES Internal Call for Research Proposals (A) 2014), 2015~2017, 15,000,000JY/year
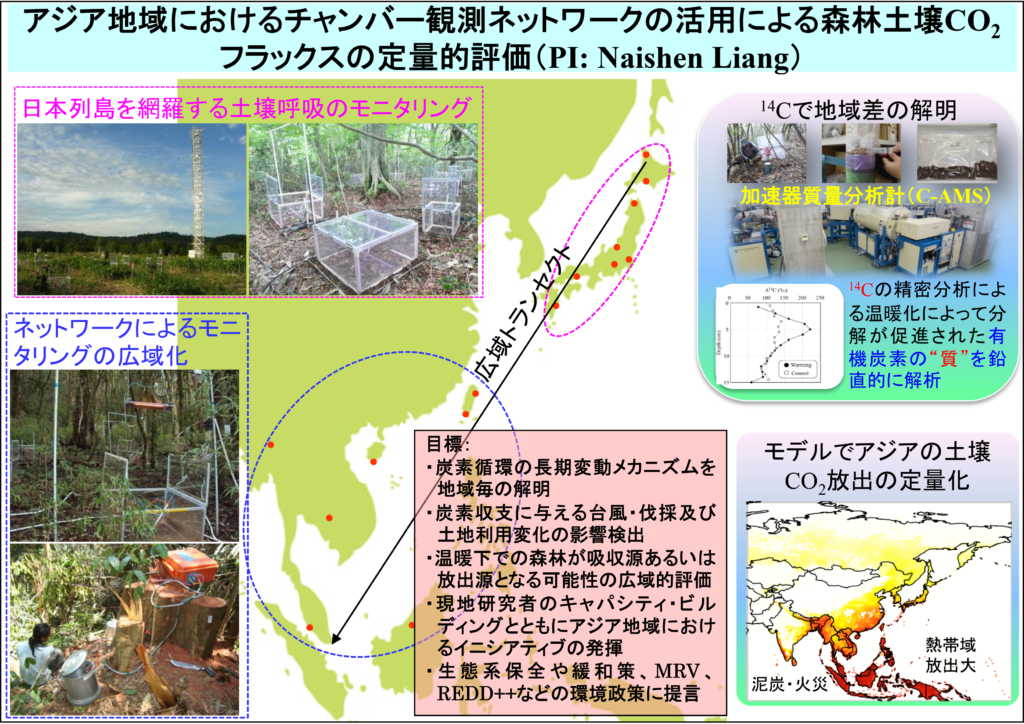
The ultimate objective of this project is to evaluate the response and feedback of Asian forest soil carbon dynamic with global warming by using an automated chamber network that developed by Dr. Naishen Liang.
- Project 3

Integrated evaluation of potential changes in both forest soil microbial biomass and compositions by using environmental DNA”,
PI: Naishen Liang
It is funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion Science and Ministry of Science (1,500,000JY/year) and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (Co-PI: Yiping Zhang, 470,000RMB), 2015~2017.
The ultimate objective of this project is to inter-comparison the effect of global warming on soil microbial biomass and compositions of subtropical forest ecosystems in both Japan and China by using a soil warming experiment network that developed by Dr. Naishen Liang.
- Project 4

Establishing Pasoh Facilities as an Observational Base for Studies on Tropical Forest Ecosystems
PI: Naishen Liang
It is funded by the National Institute for Environmental Studies of Japan, 2011~ 4,400,000JY/year.
To bring together the NIES and Malaysian leading scientists for understanding climate-related carbon cycle and biodiversity of tropical forests by strengthening Pasoh facilities as an overseas observational base.
